What is methylene blue?
Due to the blue colour, methylene blue was used as an antiseptic dye. The scientists began to test it’s efficacy against tropical diseases. In 1891, methylene blue was found to be effective against malaria. Methylene blue is effective in eliminating the persistent biofilms which are responsible for causing the disease.
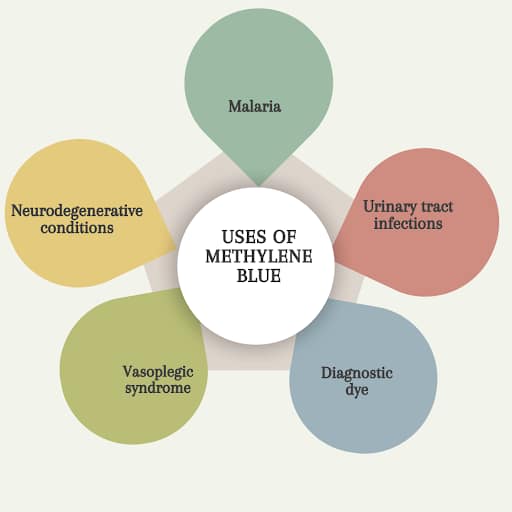
Uses of methylene blue:
- Malaria
- Urinary tract infections
- Diagnostic dye
- Neurodegenerative conditions
- Vasoplegic syndrome
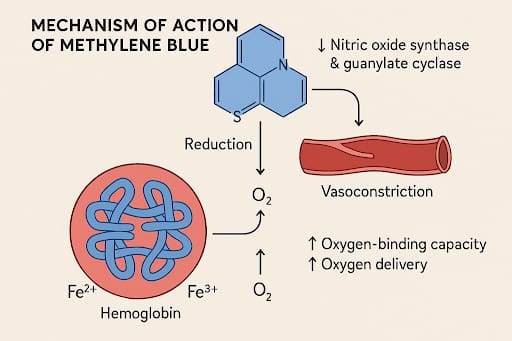
What is the mechanism of action of methylene blue?
Methylene blue reduces the oxidised form of hemoglobin (Fe3+) to Fe2+. As a result, oxygen-binding capacity of the hemoglobin will be increased that promotes the delivery of the oxygen to the tissues. Methylene blue inhibits the production of nitric oxide synthase and guanylate cyclase. This leads to decreased production of nitric oxide, causing vasoconstriction of blood vessels.
What are the adverse effects of methylene blue?
It is advisable to take methylene blue under the guidance of the doctor. Methylene blue can be associated with drug interactions, such as antidepressants. Sometimes, methylene blue can stain your teeth or turn your urine blue. The adverse effects include:
- Presence of blood in the urine
- Headache
- Altered taste sensation
- Confusion
- Pain in the extremities
Can methylene blue be used to treat Lyme disease?
Methylene blue can be used in the treatment of Lyme disease, particularly Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome. Due to its antimicrobial properties, methylene blue is effective against bacterial biofilms. Experiments indicate that methylene blue may kill Borrelia spirochetes effectively, and even in the cases of antibiotic-resistant organisms. It has great success when used along with antibiotics, that leads to clearance of bacteria.
Moreover, methylene blue is known to possess neuroprotective properties, which can be helpful to the patient with neurological symptoms caused by Lyme disease. It lowers all forms of oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, which has been linked to memory, attention, and mood improvement.
Anti-inflammatory and nitric oxide-modulating effects of methylene blue could be used to provide a degree of control over the immune dysregulation, which is common in Lyme disease patients.
How is methylene blue administered?
Oral route of administration is the most convenient route, particularly for long-term use. When orally administered, there will be systemic absorption of the drug. Therefore, it is a feasible therapeutic choice to address the chronic Lyme-related conditions including fatigue, brain fog, and neuropathic pain.
In chronic conditions, the intravenous (IV) forms can be used to achieve therapeutic levels, especially where there is a high level of neurological involvement, and when oral tolerance is a problem. Topical methylene blue cannot be employed in treating systemic Lyme disease.
Methylene blue should be administered under the guidance of a medical expert, as there is a possibility of drug interactions. Methylene blue can reduce the symptoms of Lyme disease, that offers neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties.
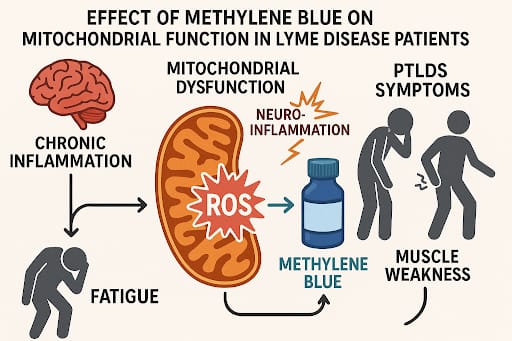
What is the effect of methylene blue on mitochondrial function in Lyme disease patients?
Due to the chronic inflammation, Lyme disease patients experience mitochondrial dysfunction. Methylene blue can improve the mitochondrial function due to the antioxidant properties. The dysfunction of mitochondria can contribute to neuroinflammation. Mitochondria produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) that carry the ability of protective mechanism.
In PTLDS patients, mitochondrial dysfunction can lead to fatigue, and muscle weakness. Methylene blue can reduce the accumulation of reactive oxygen species and minimize mitochondrial membrane damage. Hence, methylene blue plays a major role in enhancing the energy levels and reducing the clinical symptoms of Lyme disease.
Conclusion:
- Methylene blue is used as an adjunct therapy for improving the clinical symptoms of Lyme disease.
- Due to the antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, methylene blue can be used to address chronic symptoms in Lyme disease.
- Hence, methylene blue can offer hope to patients with persistent clinical symptoms.
References:
- Project Lyme. Methylene Blue For Treating Lyme Disease, Bartonella, and Babesia. Manchester (VT): Project Lyme; 30 August 2022. Available from: https://projectlyme.org/methylene-blue/
- Bistas E, Sanghavi DK. Methylene Blue. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jun 26 [cited 2025 Jun 26]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557593/
- Global Lyme Alliance. Methylene Blue and Lyme Disease [Internet]. New York (NY): Global Lyme Alliance; [date unknown; cited 2025 Jun 26]. Available from: https://www.globallymealliance.org/blog/use-of-methylene-blue-for-lyme-disease/
- Seitkazina A, Yang J-K, Kim S. Clinical effectiveness and prospects of methylene blue: A systematic review. Precis Future Med [Internet]. 2022 Dec [cited 2025 Jun 26];6(4):193–208. Available from: https://www.pfmjournal.org/journal/view.php?doi=10.23838/pfm.2022.00079


