
Can Lyme disease cause more damage to me beyond the symptoms which I will be facing?
Asked one of my friends who has been dealing with Lyme disease. Lyme disease, itself, is an autoimmune condition where the body damages its own healthy tissues unintentionally.
Understanding the stance of Lyme disease and autoimmune disorders is quite essential as it will help in managing it more effectively.
We have all the answers related to Lyme and autoimmune disorders and how exactly they are interlinked.
Can Lyme disease cause autoimmune disorders?
Lyme disease can give rise to autoimmune conditions by affecting the immune system of the body. What will this do?
- This will affect the production of antibodies and inflammatory conditions.
- However, the question of whether Lyme disease causes autoimmune disorders is a topic of limited research.
- Logically, Lyme disease does cause over-immune responses in our body. This phenomenon might as well give rise to autoimmune conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
- However, regular monitoring of the body is quite vital in saving one from suffering from an autoimmune disorder.
And even in cases if there might be a rise in autoimmune condition in the body during Lyme disease can be cured with treatment in a timely manner with treatment planning by the healthcare providers.
How Does Lyme Disease Affect the Immune System?
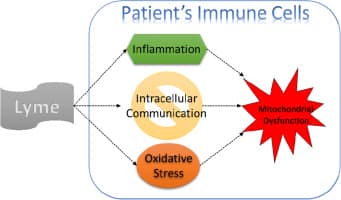
Lyme disease affects the immune system by evading immune defenses, causing persistent infection, and triggering chronic inflammation, which may impair the body’s ability to fight other illnesses.
- The immune patterns of Lyme disease are quite varied. Lyme bacteria are capable of subverting the normal immune function by modifying immune pathways hence causing protracted infection.
- This avoidance results in inflammation which persists even after the bacterial invasion has been cleared which may cause autoimmune activation.
- Additionally, Lyme disease can compromise an individual’s immune system making the patient susceptible to other infections which in turn make recovery difficult.
What Are the Common Autoimmune Effects of Lyme Disease?
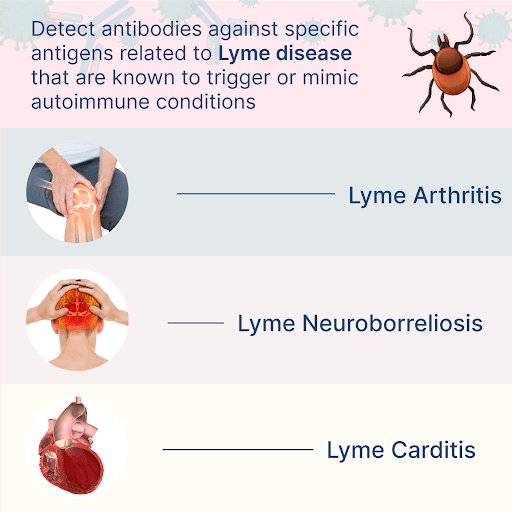
- Common autoimmune effects of Lyme disease include joint inflammation, neurological symptoms, and skin conditions like acrodermatitis. These mimic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
- The autoimmune effects of Lyme disease often resemble other chronic conditions. For instance, Lyme arthritis is associated with joint inflammation while cognitive impairment due to joint inflammation mimics Multiple Sclerosis.
- Skin problems such as chronic rash may be experienced.
All of these scenarios are considered autoimmune issues initiated by failure to control Lyme bacteria. However early management and prevention of these issues can be helpful
Can Chronic Lyme Disease Be Misdiagnosed as an Autoimmune Disorder?
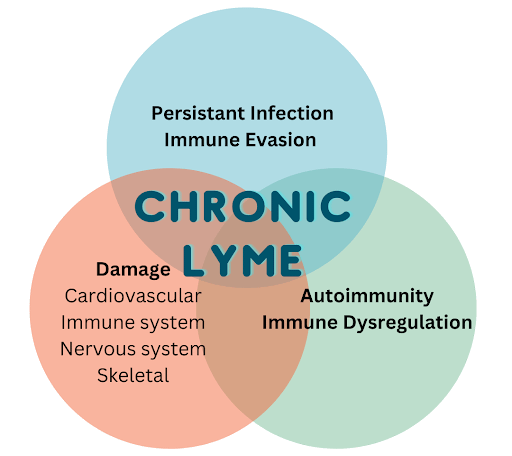
- Chronic Lyme disease can be misdiagnosed as an autoimmune disorder like lupus or fibromyalgia, leading to misdiagnosis due to overlapping symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, and neurological issues.
- Chronic Lyme disease mimics multiple autoimmune diseases making it difficult for accurate diagnosis. Overlapping features such as swelling of the joint, fatigue and brain fog contribute to misdiagnosis as a case of lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or even fibromyalgia.
- Autoimmune effects of lyme can be differentiated from primary autoimmune diseases following proper medical attention with serology and diagnostic markers for Lyme.
What are the treatment options for autoimmune effects of Lyme disease?

- Treatment is comprehensive in nature.
- Targeting the Lyme disease with antibiotics, non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs, immunomodulatory therapies can help minimize the symptoms while dealing with Lyme disease and any autoimmune conditions.
- Aiming at autoimmune effects of Lyme disease needs a twofold approach. Antibiotics to eradicate bacterial toxins.
- Drugs like corticosteroids to reduce the inflammatory responses.
- However, the conventional drug approach has always helped an individual out of a disease. But holistic or more remedial undertakings can be helpful in a steady and faster recovery route.
Can preventing Lyme disease lower autoimmune risks?

- Dealing with Lyme disease more efficiently at early stages will not lead to the chronic extension of the Lyme disease. Eventually this will lower the risk of rising autoimmune conditions in the body.
- However “Prevention is better than cure” is always the safest route. How can we prevent Lyme disease?
- Preventive measures like use of repellents/creams, periodic tick checkups, protective clothing if you stay at more tick-prone areas can directly reduce the incidence of Lyme disease.
Conclusion
- Summing up, the early detection and care is of utmost importance in preventing any autoimmune conditions due to Lyme disease.
- Consulting a healthcare provider for the medicinal approach is however vital. Being cautious with the symptoms can be helpful in early detection.
References
- Lyme Disease Diagnosis. Johns Hopkins Lyme Disease Research Center. Available from: Link
- Dr. Will Cole. 11 effective home remedies for Lyme disease. drwillcole.com. 11 Effective Home Remedies For Lyme Disease.
- Alliance GL. Home [Internet]. www.globallymealliance.org. Available from: Link
- King R. 5 Strategies for Coping with Chronic Illness | Frequencell Inc. [Internet]. Frequencell Inc. 2023. Available from: Link


